Introduction
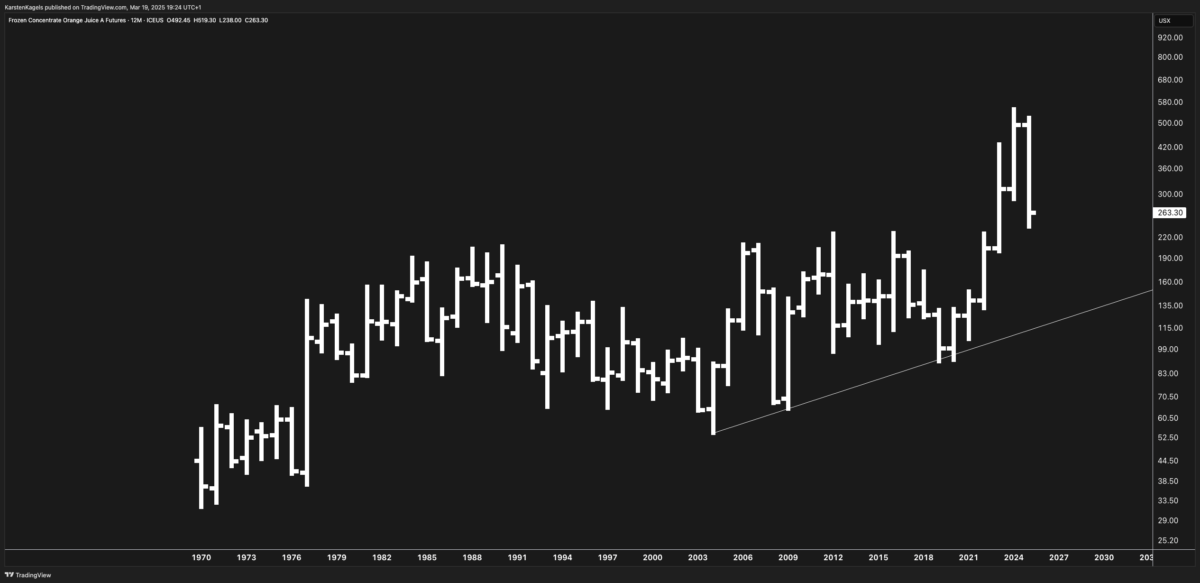
The chart displays the long-term price history of Frozen Concentrated Orange Juice A Futures (OJ) from approximately 1970 to the present, with projections into 2030. What’s immediately apparent is a significant price surge in recent years, particularly from 2021 to 2024, where prices reached historic highs approaching the $300 mark. This analysis will explore key technical patterns, fundamental drivers, and provide multi-scenario forecasts for orange juice futures.
Technical Analysis
Major Price Patterns & Levels
The orange juice futures market demonstrates several distinct technical phases:
- 1970s-1980s Consolidation: Prices traded primarily in a range between approximately $30 and $150, establishing a long-term support base.
- 1980s-1990s Trading Range: A more defined trading range emerged between roughly $70 and $180, with multiple tests of both support and resistance.
- 2000s-2010s Sideways Channel: Prices remained largely range-bound between $60 and $220, with occasional breakouts that failed to sustain momentum.
- 2021-2024 Parabolic Advance: The most striking feature is the recent explosive move to all-time highs above $400, followed by a sharp correction to current levels around $250-280.
- Long-Term Uptrend Line: A clear multi-decade support trendline can be drawn from the lows of the 1970s through subsequent major bottoms, which currently intersects around the $150-170 area.
Support & Resistance Levels
Key Support Levels:
- $250: Recent reaction low and psychological level
- $220: Multiple historical pivot points
- $150-170: Long-term uptrend line and historical congestion zone
- $100: Major psychological support and historical floor
Key Resistance Levels:
- $300: Recent reaction high and psychological level
- $350-420: All-time high zone
- $500: Projected extension target
Fundamental Drivers
Supply & Demand Dynamics
The dramatic price increase in orange juice futures since 2021 can be attributed to several fundamental factors:
- Citrus Greening Disease (HLB): This bacterial disease has devastated Florida’s orange crop over the past decade, reducing output by more than 70% from historical averages. It continues to threaten global production.
- Extreme Weather Events: Hurricane damage in Florida and freezes in key growing regions have compounded supply problems.
- Brazilian Production Issues: As the world’s largest producer, Brazil has faced its own challenges with drought and disease, limiting its ability to offset U.S. shortfalls.
- Rising Production Costs: Inflation in agricultural inputs, labor, and transportation has driven producer costs higher.
- Stable Consumer Demand: Despite price increases, orange juice consumption has remained relatively stable due to its perceived health benefits.
Macroeconomic Considerations
Several broader economic factors will influence future price action:
- USD Strength/Weakness: The dollar’s value significantly impacts commodities like orange juice, with a weaker dollar typically supporting higher prices.
- Climate Change Impact: Increasing frequency of extreme weather events poses ongoing risks to production.
- Health Trend Sustainability: Continued consumer interest in vitamin C and immune-boosting beverages supports demand.
- Inflationary Environment: Higher general inflation could support continued strength in agricultural commodities.
Multi-Scenario Forecast
Bullish Scenario (30% Probability)
If citrus greening disease continues to spread and weather patterns remain unfavorable, while demand remains stable:
- Short-term (6-12 months): Retest of the $350-420 resistance zone
- Medium-term (1-3 years): Breakout above $420 targeting $500-550
- Long-term (3-5 years): Potential move toward $600-700 if structural supply issues persist
Catalysts: Major freeze event in Brazil, acceleration of citrus greening, significant reduction in global inventories.
Neutral Scenario (50% Probability)
If current supply constraints moderately improve and demand remains stable:
- Short-term (6-12 months): Consolidation between $220-320
- Medium-term (1-3 years): Gradual upward drift toward $300-350
- Long-term (3-5 years): Continued range-bound trading with an upward bias, averaging $280-380
Catalysts: Moderate success in disease management, average weather conditions, balanced supply/demand dynamics.
Bearish Scenario (20% Probability)
If there are significant breakthroughs in disease resistance or substantial increases in global production:
- Short-term (6-12 months): Decline to test the $200-220 support zone
- Medium-term (1-3 years): Potential test of the long-term trendline around $150-170
- Long-term (3-5 years): Return to the historical trading range of $150-250
Catalysts: Disease-resistant varieties gaining traction, expansion of production in alternative regions, demand destruction from sustained high prices.
Comparative Market Analysis
Relationship with Other Agricultural Commodities
Orange juice futures have significantly outperformed most other agricultural commodities since 2021. While many agricultural markets have seen price increases, OJ’s move has been particularly dramatic due to its specific supply challenges.
Coffee: Both markets face disease and climate challenges, but orange juice has seen more severe production disruptions.
Sugar: Often correlated with orange juice as another tropical agricultural product, but with more diversified global production.
Trading Strategy Considerations
- Pairs Trading: Consider paired positions with other citrus or fruit juice commodities to hedge specific risks.
- Seasonality: Orange juice typically shows seasonal strength during the Northern Hemisphere winter (Dec-Feb) when freeze risks are highest.
- Options Strategies: The high volatility in OJ futures makes options strategies particularly attractive, including:
- Selling put options at major support levels
- Using call spreads to participate in upside with defined risk
- Using strangles or straddles ahead of key USDA crop reports
Market Sentiment & Positioning
Commercial producers and processors have maintained significant short hedges, reflecting their expectation that current elevated prices may not be sustainable long-term. However, managed money positions have fluctuated between net long and net short, suggesting uncertainty about immediate direction.
The retail trader sentiment has been predominantly bullish, often a contrarian indicator suggesting caution about immediate upside potential.
Beginner’s Guide to Orange Juice Futures
Frozen Concentrated Orange Juice futures (trading symbol: OJ) are agricultural commodity futures contracts traded primarily on the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE). Each contract represents 15,000 pounds of orange solids.
The market gained pop culture fame through the 1983 movie “Trading Places,” but remains a serious and important market for:
- Juice Processors: Who use futures to hedge production costs
- Citrus Growers: Who hedge future production
- Speculators: Who seek to profit from price movements
- Food Companies: Who manage ingredient costs
Traders should monitor:
- USDA crop production reports
- Brazil’s export numbers
- Weather forecasts for Florida and São Paulo state
- Quarterly juice consumption figures
Conclusion & Actionable Insights
The orange juice futures market has undergone a fundamental transformation due to persistent supply challenges. While current prices are historically high, structural problems with citrus production suggest a “new normal” price range well above historical averages.
For Traders:
- Use pullbacks to the $220-250 range as potential entry points for long positions
- Consider collar strategies (protective puts) if taking long positions at current levels
- Monitor the long-term trendline around $150-170 as a critical technical level
For Hedgers:
- Producers should consider locking in current historically favorable prices
- Processors may benefit from scale-in buying strategies on dips toward support levels
FAQ
Q: What are the biggest risks to orange juice prices in the next year? A: Weather events (particularly freezes), progression of citrus greening disease, and consumer response to sustained high retail prices are the primary risks.
Q: Is the current price level sustainable? A: Current prices reflect genuine supply constraints that will likely persist for several years, making a return to pre-2020 price levels unlikely in the near term.
Q: How does climate change affect orange juice futures? A: Climate change increases volatility through more frequent extreme weather events in growing regions, including both freezes and droughts, adding risk premium to prices.
Q: How can small investors participate in the orange juice market? A: Besides futures contracts, investors can consider stocks of companies with significant exposure to citrus production or processing, or ETFs that include agricultural commodities.