Table of Contents
Anzeigen
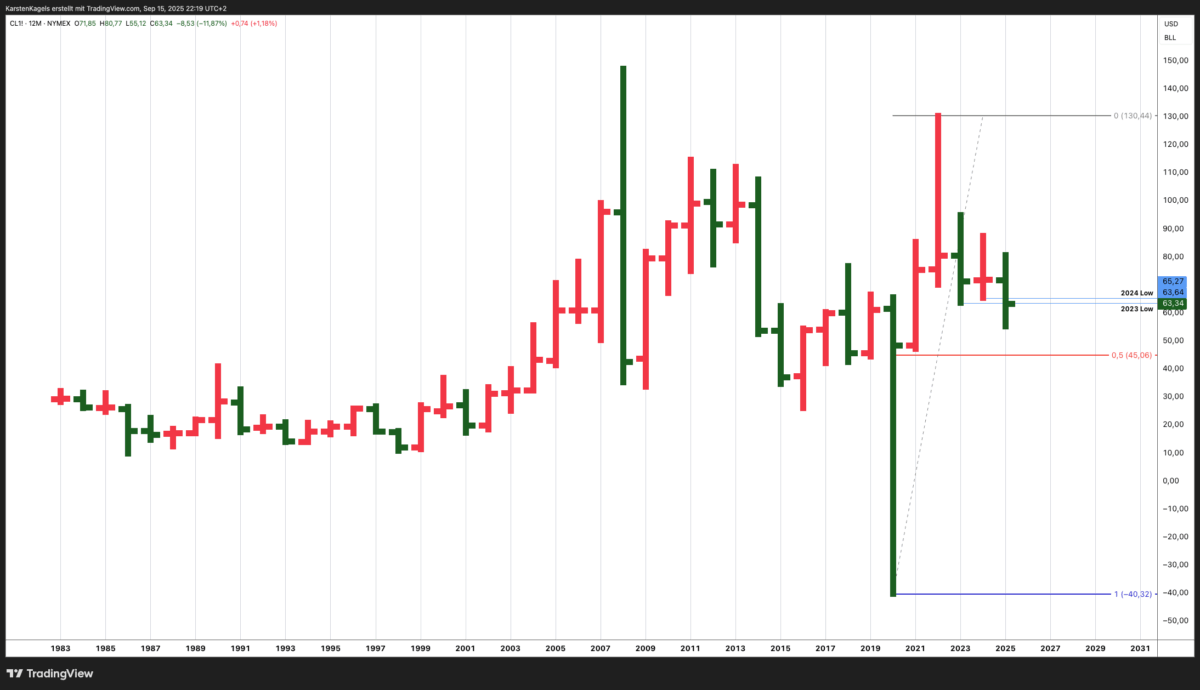
Fibonacci Retracement and Important Yearly Lows
The provided chart displays the long-term price action of Light Crude Oil futures (WTI) from 1983 to 2025, showing historical price movements and potential future projections.
Currently trading around $63.34, WTI crude has experienced significant volatility throughout its history, with dramatic price swings reflecting the complex interplay between geopolitical events, supply-demand dynamics, and macroeconomic factors.
Important price levels are now the low of the years 2003 at $63.64 and 2004 at $65.27. Below this critical price levels, the market stays bearish. The longer price forecast shows downside potential to the 50 % Fibonacci Retracement at $45.06, a little below the low of 2021 at $47.18.